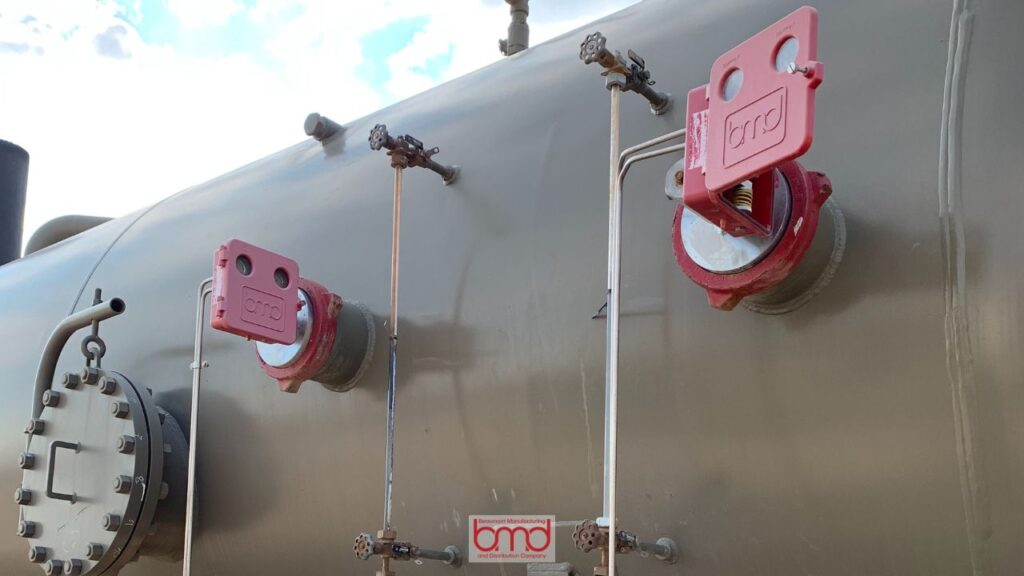
Introduction
Regular maintenance of pressure regulators is crucial for ensuring efficient and reliable operation, given their essential role in controlling oil and gas production equipment. Properly maintained regulators help minimize pressure fluctuations, prevent system failures, and optimize performance—keeping your operations running seamlessly.
At Beaumont Manufacturing and Distribution Company (BMD), we specialize in high-performance regulators designed for upstream and midstream applications. Headquartered in Texas, we manufacture a diverse range of pressure-reducing regulators, back pressure regulators, and specialty models—all engineered with durability, safety, and efficiency in mind.
This post provides BMD-specific maintenance tips to help industry professionals achieve peak regulator performance. From routine inspections to best practices, following these guidelines can ensure smooth operations, reduce downtime, and extend equipment lifespan.
II. Why pressure regulator maintenance Matters in Oil & Gas Operations
Oil and gas production systems are characterized by inherently unsteady flow dynamics. Regulators play a critical role in controlling pressure in oil and gas operations, ensuring system stability, and maintaining safety in oil and gas operations. Poorly maintained regulators may cause unacceptable pressure fluctuations, leading to equipment damage, unexpected shutdowns and safety hazards. Failure of regulators can lead to serious consequences, such as leaks, fires, or explosions in hydrocarbon production environments.
By adhering to routine inspections and proactive servicing, operators can minimize risks, improve system reliability, and maximize regulator lifespan, ensuring continuous and safe operations in demanding environments.
From a compliance standpoint, pressure regulators in natural gas transmission and distribution must undergo regular inspections and testing to meet industry standards. Routine maintenance reduces the risk of non-compliance, protecting companies from potential legal issues and fines.
III. Understanding BMD’s Regulator Design
Beaumont Manufacturing and Distribution Company (BMD) produces a broad range of direct-acting and pilot-operated pressure regulators, designed for various applications in the oil and gas industry.
Direct-acting regulators feature a simple yet robust design, comprising a loading spring, diaphragm, and disk-seat assembly, which collectively handle loading, sensing, and flow control. Their straightforward construction ensures quick responsiveness and exceptional reliability for pressure reducing as well as back pressure control applications.
Pilot-operated regulators, while more complex, offer greater capacity and precise control. These regulators use a smaller direct-acting pilot to sense process pressure and operate the main regulator. Instead of responding directly to process pressure, the main regulator’s diaphragm moves based on signals from the pilot, making it ideal for high-flow capacity and precision control applications.
Direct-acting pressure regulators are the most widely used type, valued for their simplicity, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Their design ensures reliable operation with minimal complexity.
Below are the key components that define their functionality:
Valve Body –The valve body is the primary component housing internal elements such as the plug, seat, and stem, which regulate fluid flow. Direct-acting, spring-loaded BMD regulators use a disk-and-seat arrangement to control flow by adjusting the cross-sectional area between the disk and seat.
Actuator – In industrial parlance, an actuator converts pressure signals into mechanical movement, adjusting the relative positions of the disk and seat to vary fluid flow resistance. In direct-acting, spring-loaded BMD regulators, the actuator is made up of the spring, diaphragm, diaphragm adaptor, and linkage. . The difference between process pressure and the spring force acts on the diaphragm to create an unbalanced force, which is transmitted to the disk via a diaphragm plunger, linkage, and stem. This movement causes the disk to shift closer to, or farther from, the seat regulating fluid flow through the valve.
Diaphragm Housing–This housing contains the diaphragm adaptor and linkage. It allows the diaphragm to be exposed to the downstream pressure which counteracts force from the spring on the opposing side.
Spring Housing – This chamber houses the spring and adjusting screw. The spring provides the reference force, also known as the set pressure, which acts on the diaphragm to maintain proper regulation.
Diaphragms & Seals – These components ensure leak-tight performance and responsiveness to pressure changes, maintaining system integrity and efficiency.
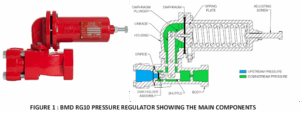
Figure 1 illustrates BMD’s RG10 pressure-reducing regulator, showing its various components.
The unique features of BMD regulators that make them easy to maintain are as follows:
Simple Designs: Our engineers and technicians have extensive first-hand field experience, and our regulator designs incorporate practical lean engineering to enhance reliability and simplify maintenance.
Durable materials: BMD regulators use high-quality materials including corrosion-resistant alloys, specialty elastomers, polymers and coatings. These materials ensure durability in demanding applications and harsh environments, thus reducing the maintenance burden for operators.
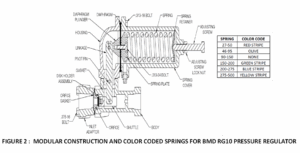
Modular Construction: BMD pressure regulators feature a modular design, allowing quick and easy replacement of individual parts, reducing maintenance downtime. Spares and replacements can be effortlessly ordered via BMD’s part identification system, while color-coded springs help prevent errors during replacement. Figure 2 illustrates these aspects.
IV. Routine Pressure Regulator Maintenance Schedule
BMD provides comprehensive installation, operation, and maintenance instructions for each regulator model, along with a standard repair kit. To ensure optimal performance and safety, the following maintenance schedule is recommended:
Daily: Conduct a quick visual inspection for leaks. Identifying leaks early helps mitigate safety and performance risks.
- A leak at the diaphragm indicates diaphragm failure and requires prompt replacement.
- Flange leaks necessitate gasket or o-ring replacement.
- Leaks at threaded connections require checking the threads, removing debris, and tightening with pipe thread compound.
Monthly: Perform a detailed visual inspection for any damage to the body and housing without dismantling the regulator. Assess its performance—if the seat fails to seal properly, pressure regulation will be ineffective. In such cases, the disk holder assembly must be replaced.
Quarterly: Conduct a thorough examination of all connections, seals, springs, diaphragms, and moving parts. Clean components using approved solvents, avoiding harsh chemicals that could degrade materials. Lubricate moving parts according to BMD guidelines.
Annually: Replace diaphragms and seals to ensure consistent, reliable performance.
V. Best Practices for pressure regulator maintenance
Adopting the following best practices will ensure that your BMD regulators remain reliable, safe, and efficient in operation:
Use Only OEM Parts: Always replace components with BMD-approved OEM parts to ensure compatibility and optimal performance.
Document Maintenance Activities: Ensure that the appropriate and latest updates of standard procedures are issued to maintenance staff, Keep detailed records for regulatory compliance and operational efficiency.
Employ Trained Field Staff: Ensure technicians are trained on BMD-specific procedures to ensure proper handling and longevity. Ensure adequate field supervision by experienced staff.
Avoid Common Mistakes: Prevent issues like overtightening, which can damage seals, and using incorrect lubricants, which may lead to malfunction.
VI. When to Replace vs. Repair a BMD Regulator
BMD regulators are manufactured for durability, and a standard repair kit allows for component replacement. However, in certain cases, full regulator replacement is essential to ensure safety and efficiency.
Signs a Regulator Needs Full Replacement
- Severe corrosion compromising structural integrity.
- Cracked housing or damaged internal components.
Situations where a Rebuild Kit Is Sufficient
- Minor wear on seals or diaphragms.
- No structural damage or cracks in the valve body, housing and connections.
- Minor external corrosion which can be resolved by fresh protective coating.
- The pressure regulator is assessed to be safe and meets performance specifications after minor repairs.
Balancing Cost vs. Risk
Most major operators typically maintain a risk matrix that clearly defines risk evaluation criteria and corresponding risk levels. These should be used in conjunction with your own judgment. Generally, the following principles apply.
- Rebuilding is cost-effective for minor issues.
- Replacing prevents costly failures and ensures long-term reliability.
- Ignoring warning signs can lead to system breakdowns and safety hazards
VII. Support and Resources from BMD
All BMD products are accompanied by comprehensive maintenance manuals and training materials. Additionally, our customers benefit from outstanding support services provided by our team of highly skilled technicians, field service professionals, and expert engineers.
Repair kits can be ordered by contacting BMD or one of its distributors. It is best to provide a serial number and model code of the unit for which the repair kit is needed.
VIII. Conclusion
Regular maintenance of pressure regulators is crucial in oil and gas operations to ensure safety, efficiency, and equipment longevity. Follow proactive inspection schedules and BMD’s best practice recommendations.
BMD’s support team is always ready to tackle your toughest maintenance challenges. Maximize reliability and safety with BMD’s expert assistance—contact us today for support or to schedule a consultation.




